What is "Heatwave"?
What is "Heatwave"?
CHONG Man-lok, KONG Wai
October 2021
Under global warming, extreme weather events, such as extreme high temperatures, have become more frequently. From time to time, we learned from the media that a region was hit by "heatwave" with record-breaking temperatures. So, what is "heatwave"? How does "heatwave" bring abnormal hot weather?
"Heat" in the first part of the word "heatwave" refers to temperatures higher than the climatological normal of an area. When those anomalous high temperatures sustain for a certain period of time, the situation will be named as "Heatwave". As the characteristics of climate vary place by place, there is no universal definition of "heatwave" in terms of the degrees of temperature above the climatological normal and the duration.
Some may have mistaken heatwave as a weather system, being the "cause" of persistent and abnormal hot weather. Indeed, heatwave is a phenomenon, and it does not "hit" or "depart" from a place like a weather system. Its spread and persistence depend on the weather systems that give rise to the heatwave. In other words, heatwave is the "effect" instead of the "cause" of persistent and abnormal hot weather. For example, heatwaves over mid to high-latitude regions are usually caused by blocking[1]. Under blocking pattern, the atmospheric circulation becomes relatively stagnant. Subsiding air of the ridge of high pressure inhibits cooling. Together with hot air mass being transported from low latitudes to mid and high latitudes, such pattern is conducive to sustained hot weather in summer.
The heatwave that started affecting the northwestern part of North America in late June 2021 was in fact a result of blocking. Figure 1 shows temperatures over some places in the northwestern part of the United States and the southwestern part of Canada were more than 10 degrees above the climatological normal. Lytton, a village located in the southern part of British Columbia, Canada, even recorded a record-breaking temperature of 49.6 ℃, which was also the highest ever observed in Canada[2].
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures will cause heat exhaustion, as well as deterioration of health conditions of some patients with chronic diseases[3], leading to fatalities. Over 10,000 deaths were attributed to the heatwave over Russia in July 2010[4]. Besides, increase of electricity demand over cities and possibility of crop failure are also some socio-economic impacts of heatwaves.
Researches revealed that heatwaves are very likely to occur with higher frequency and longer duration under global warming[5]. We must take every effective measure now to save energy and reduce emissions, in an effort to slowing down global warming, and to adapt to climate change and combat against extreme weather. Otherwise, mankind will face the unbearable consequences.
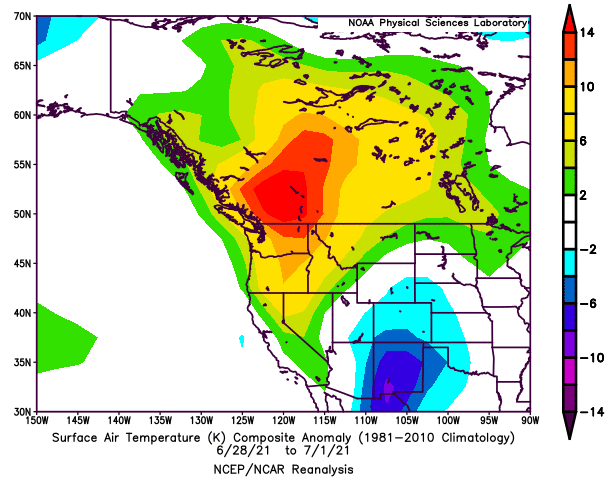
Figure 1: Temperature anomalies over North America in late June to early July 2021. Temperatures above 10 degrees of the climatological normal are represented by orange and red colours. (Source: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration of the United States)
References:
[1] Cool Met Stuff: Omega Blocks (in Chinese only)
[2] Royal Meteorological Society: Record-breaking heat in Canada
[3] World Meteorological Organization: Heatwaves and Health: Guidance on Warning-System Development
[4] Hong Kong Observatory: Extreme weather events
[5] The Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: The Synthesis Report, SPM2.2
[1] Cool Met Stuff: Omega Blocks (in Chinese only)
[2] Royal Meteorological Society: Record-breaking heat in Canada
[3] World Meteorological Organization: Heatwaves and Health: Guidance on Warning-System Development
[4] Hong Kong Observatory: Extreme weather events
[5] The Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: The Synthesis Report, SPM2.2