What causes a rainbow?
What causes a rainbow?
HUNG Fan-yiu
What causes a rainbow?

(Photo taken by observer at Airport Meteorological Office, Hong Kong Observatory, 26 July 2003)
A rainbow picture is usually taken with sunlight from the back of the photographer.
Sunlight is made up of light of every wavelength (loosely, colour). When there are water droplets in the atmosphere, for instance when rain has fallen, sunlight will get refracted (i.e. bent) in a water droplet. Blue light has a shorter wavelength and is refracted more than light with a longer wavelength such as red light. For this reason, blue (red) light is located in the inner (outside) part of the rainbow.
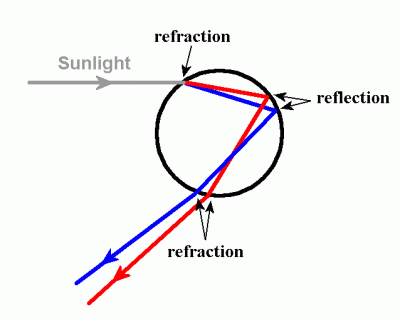
Each of the colours in the rainbow comes to the eye from a different set of water droplets.
Sometimes we can see a double rainbow. What causes it?

(Photo taken by observer at Airport Meteorological Office, Hong Kong Observatory, 26 July 2003)
When light passes through a water droplet, it gets refracted, reflected and then refracted again. The rainbow which we normally see (i.e. primary rainbow) results from one reflection inside a droplet.
A secondary rainbow is produced when there are two reflections inside a droplet.
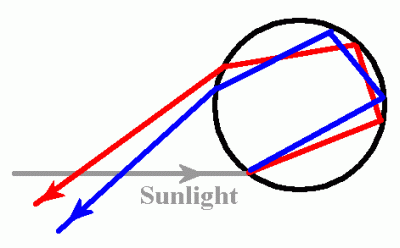
Why is the colour sequence reversed in the secondary rainbow?
The diagram above also explains why the colour sequence is reversed when compared with a primary rainbow. The secondary rainbow is less bright because some light energy is lost at each reflection.

(Photo: Wah Kiu Yat Po, 3 August 1993)
In the photo above, do you notice that the region outside the primary rainbow looks much darker than that inside the primary rainbow? See here.