Anemometer along the runway
| The anemometer installed on airport uses a vane to measure the wind direction and a cup to measure the wind speed. The Hong Kong Observatory operates three anemometers along each of the three runways of the Hong Kong International Airport.
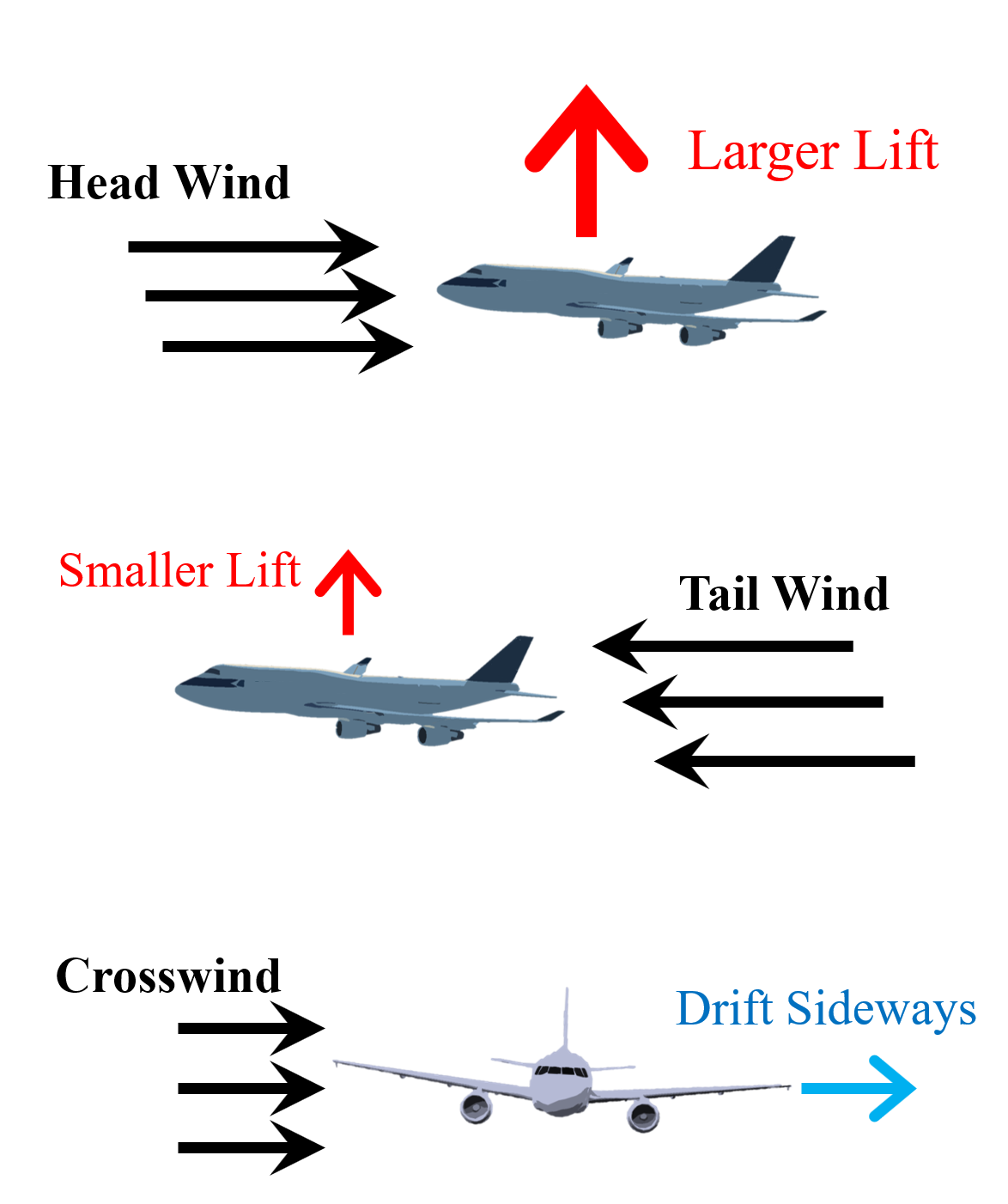
"Head wind" refers to the wind blowing opposite to aircraft motion and provides larger lift for an aircraft. Wind blowing along aircraft motion, known as "tail wind", gives smaller lift. An increasing head wind or a decreasing tail wind leads to additional lift. "Crosswind" is the wind component at right angle to the flight path, causing an aircraft to drift either to the left or right of the intended path. |
 |