Radiation Tidbits - China's future development of nuclear energy
Written by: Yeung Siu-wai
China has a well-established system for the nuclear industry and is now expanding its nuclear power facilities in accordance with the "Medium and Long Term Nuclear Power Development Plan (2005-2020)" approved by the State Council. The plan provided specific recommendations and implementation programs for the future development of nuclear energy in China. This article introduces some main issues of the plan.
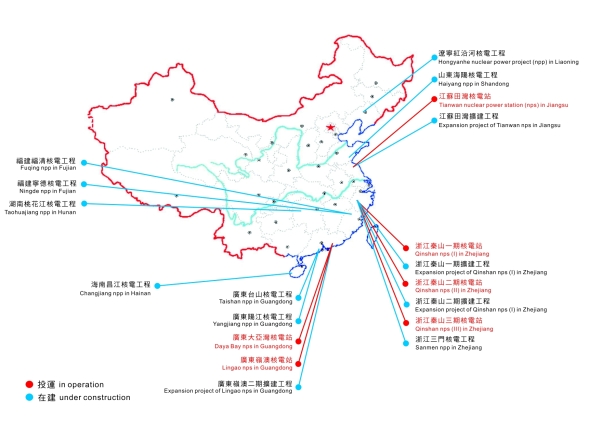
Nuclear power plants in operation and under construction in China
- Does China need to develop nuclear power?
- Is China capable of enhancing the development of nuclear power?
- What are the main development areas of China's nuclear power?
- Does China need to develop nuclear power?
Nuclear power is an economic, clean and efficient energy. The fuel cost is only about 20% of the cost of electricity generation. Compared with thermal power, nuclear power does not discharge pollutants such as sulphur dioxide, smoke and carbon dioxide. Partial substitution of coal-fired power by nuclear power can reduce emission of pollutants and slow down global warming.
Energy resources are unevenly distributed in China. Development of nuclear power can improve the structure of energy supply in China, provide stable supply of electricity, and reduce problems on logistics and environment due to the production and transportation of coal.
Nuclear power is a high technology industry. Promoting nuclear power facilities is favorable to advancing technology of the country to a level on a par with international standard.
- Is China capable of enhancing the development of nuclear power?
China began to develop nuclear power since the 70s in the 20th century. The first self-designed and self-built nuclear power plant began operation in the early 90s. Until now, China has 6 nuclear power plants, consisting of 11 reactors, throughout the country. They maintain a power capacity of more than 9 million kilowatts. With years of joint efforts by various departments, China acquired skills and good achievement in the design, construction and operations management of pressurized water reactors. In addition, China had considerable experience in securing nuclear fuel supply, exploring nuclear technology and establishing safety regulations and emergency response system. These collectively contribute to a good foundation for nuclear power development.
The resources of uranium in China are rich. About half of the land in China has not been prospected for uranium yet. It is believed that uranium resource will not be an obstacle to the development of nuclear power.
The "Medium and Long Term Nuclear Power Development Plan (2005-2020)" was an important document guiding nuclear power development in China. It proposed the principles, measures and targets of nuclear power development. It also elaborated on the technical roadmap of nuclear power development, strategy of autonomy development and schedule of nuclear power construction. It put forward concrete implementation programs for the safety measures and policies required in carrying out the plan, leading to a sustainable development of nuclear industry in China.
- What are the main development areas of China's nuclear power?
Currently, the 6 operational nuclear power plants in China run a total of 11 reactors and the total nuclear power capacity is over 9 million kilowatts, accounting for only 2% of the country's total power generation capacity. By 2020, according to the "Medium and Long Term Nuclear Power Development Plan (2005-2020)", China will build more nuclear power plants in 13 priority sites selected from coastal provinces like Guangdong, Zhejiang, Shandong, Jiangsu, Liaoning, Fujian and Guangxi, giving a total installed nuclear power capacity of 40 million kilowatts. The annual nuclear power output by that time will reach 260 billion kilowatt-hours, contributing to more than 6% of the country's total power generation capacity. It is even anticipated that the target can be adjusted upward in light of the present nuclear power construction.
In the long run, tens of nuclear power plants will be built in the coastal areas such as Guangdong, Zhejiang and Fujian, as well as in inland areas like Hubei, Hunan, and Jiangxi. As the economy of inland cities grows and their demand for electricity increases, it is necessary to expedite the development of inland nuclear power plant and, through international cooperation, introduce and master the design and equipment manufacturing technology of the third generation million-kilowatt pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant. This type of reactor has four safety barriers and multiple safety protection systems, providing a very high level of safety for inland nuclear power plant.
China will continue the "three-step" approach in nuclear energy development, i.e. thermal neutron reactor - fast neutron reactor - controlled nuclear fusion reactor. At present, development of nuclear power generation mainly concentrates on thermal neutron reactors. At the same time, the study of fast neutron reactor will be expedited. There will also be a plan for exploring the technology of controlled nuclear fusion reactor.
During the course of nuclear power construction, China will also construct low- and intermediate-level radioactive waste disposal sites in parallel to handle the ever increasing low- and intermediate-level radioactive wastes resulted from the development of nuclear power. By 2020, an underground repository for storing high-level radioactive wastes will also be built.
 Back to Top
Back to Top