Basic dosimetric quantities
Absorbed dose
Absorbed dose is one of the fundamental dosimetric quantities in radiation protection. It is a physical quantity to measure radiation energy absorbed by unit mass of materials.
- Definition:
- Energy absorbed per unit mass of the material
- Unit:
- Gray (Gy)
Equivalent dose
Biological effects are attributed not only to the absorbed dose but also depend on the type and energy of the radiation. Equivalent dose is a physical quantity to measure the effect to a tissue or organ by different types and energies of radiation.
- Definition:
- For a particular type and energy of radiation, equivalent dose is the absorbed dose averaged over a tissue or organ and weighted for the radiation quality that is of interest. The weighting factor for this purpose is called "radiation weighting factor", which reflects the severity of biological effects due to different types and energies of radiation. When the incident radiation field consists of different types and energies of radiation, the equivalent dose in a tissue or organ is equal to the sum of the weighted absorbed doses.
- Unit:
- Sievert (Sv)
| Radiation type | Radiation weighting factor |
|---|---|
| Photons | 1 |
| Electrons and muons | 1 |
| Protons and charged pions | 2 |
| Alpha particles, fission fragments, heavy ions | 20 |
| Neutrons | A continuous function of neutron energy (see Fig. 1 and Eq. 4.3) |
All values relate to the radiation incident on the body or, for internal radiation sources, emitted from the incorporated radionuclide(s).
Source : 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP Publication No. 103)
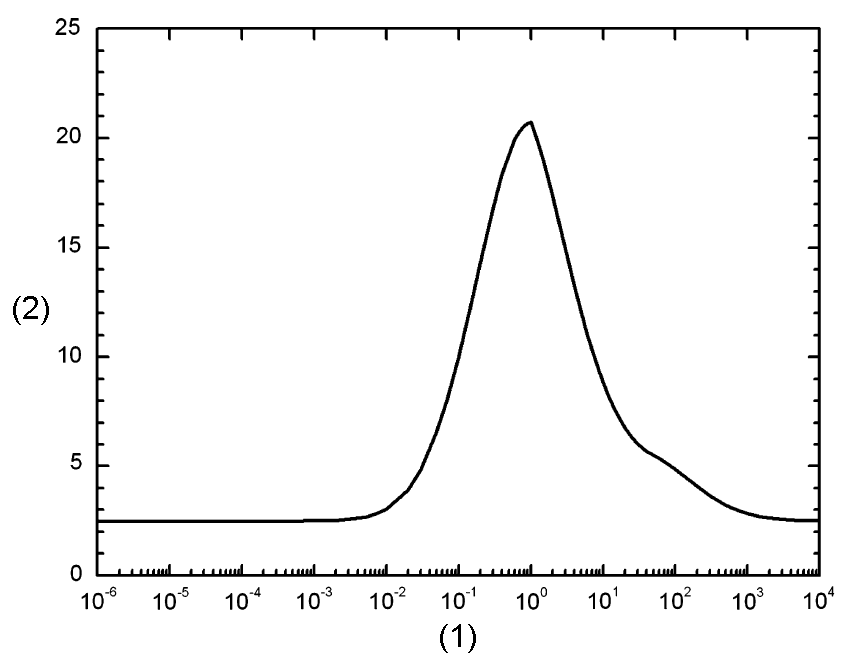
Fig. 1: Radiation weighting factor for neutrons versus neutron energy.
In picture, (1) is Neutron energy/MeV; (2) is Radiation weighting factor
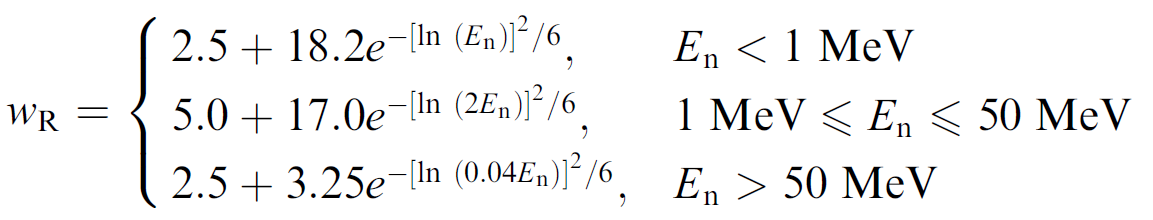
Eq. 4.3: The continuous function in neutron energy recommended for the calculation of radiation factors for neutrons.
Effective dose
Biological effects also depend on the type of tissue or organ that has been irradiated. Effective dose is to quantify the total detriment from exposures of several organs or tissues.
- Definition:
- Effective dose is the sum of the weighted equivalent doses in all the tissues and organs of the body. The factor by which the equivalent dose in tissue or organ is weighted is called "tissue weighting factor", which represents the relative contribution of that organ or tissue to the total detriment resulting from uniform irradiation of the whole body.
- Unit:
- Sievert (Sv)
| Tissue | Tissue weighting factors | Sum of tissue weighting factors |
|---|---|---|
| Bone marrow (red), Colon, Lung, Stomach, Breast, Remainder tissues* | 0.12 | 0.72 |
| Gonads | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Bladder, Oesophagus, Liver, Thyroid | 0.04 | 0.16 |
| Bone surface, Brain, Salivary glands, Skin | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Total | 1.00 |
* Remainder tissues: Adrenals, Extrathoracic (ET) region, Gall bladder, Heart, Kidneys, Lymphatic nodes, Muscle, Oral mucosa, Pancreas, Prostate(♂), Small intestine, Spleen, Thymus, Uterus/cervix(♀)
Source : 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP Publication No. 103)