Heat stress in Hong Kong due to urbanization effect
28 May 2008
The Hong Kong Observatory joined hands with the Geography Department of the University of Hong Kong (HKU) to study the heat stress in Hong Kong due to urbanization effect. The Observatory's mobile survey vehicle, equipped with Global Positioning System (GPS) and Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) heat stress measurement system, was deployed together with six vehicles equipped with GPS, temperature and humidity measurement instruments of the HKU to traverse the busy streets in Kowloon and Hong Kong Island to gather temperature and heat stress data over different parts of Hong Kong.
Recent studies carried out by the Observatory show that the rising trend of air temperature in Hong Kong is influenced by both the global warming due to greenhouse effect and the urban development in Hong Kong. As the latter might depend significantly on the building density and land use, this study aims to better understand the spatial variability of heat stress in Hong Kong due to urbanization.
As part of the study, two vehicle traverses were conducted on the afternoon of 22 and 23 May 2008. More joint vehicle traverses would be conducted in future to study the spatial variability at different times of the day and different weather conditions.
The Observatory's mobile survey vehicle and the instrumented vehicle of the University of Hong Kong (the taxi behind) traversing the central business districts in Kowloon.
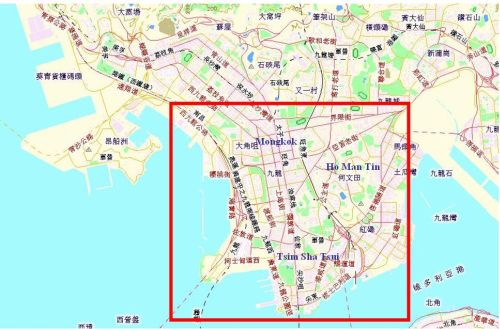
The region covered by the Observatory's survey vehicle to study heat stress due to urbanization on the afternoon of 22 and 23 May 2008.