The Looks of Water in Winter
The Looks of Water in Winter
PAN Chi-kin
March 2012
Hong Kong is situated in the sub-tropical zone at the latitudes similar to those of Hawaii. However, the temperature variation of Hong Kong within a year is larger than that of Hawaii. In Hong Kong, the monthly mean temperature during summer is different from that in winter by more than 10oC. Located at the southeastern edge of the vast Asian continent, Hong Kong's weather conditions in winter are also quite different from other sub-tropical regions. In winter, cold air mass accumulates over the central and northern regions of the Asian continent such as Siberia. As the continent cools down more quickly than the ocean, winter monsoon establishes itself, blowing from the land toward the sea, advecting the cold air from the northern region to the coastal areas and bringing cold weather to Hong Kong.
When the cold winter monsoon reaches Hong Kong, local temperature will drop significantly. Under certain weather conditions, frost may appear over rural areas and on high ground. Frost is a weather phenomenon which can be in general classified into three types: hoar frost (mainly caused by radiation cooling, also known as radiation frost), advection frost and rime. In Hong Kong, hoar frost occurs more frequently than the others. Let's focus on this type of frost here. In the early morning of cold season, the thin layer of white ice crystals appearing on the grass or soil might be hoar frost. The occurrence of hoar frost not only depends on weather conditions, but also the nature of the object surface. When the object is chilled by radiation cooling, the surface temperature will drop rapidly and the temperature of surrounding air close to the object will remain relatively high. The air will be chilled and simultaneously releases the excessive water vapour. When the temperature drops to 0oC or below, water vapor condenses through deposition directly on the surface as ice crystals, i.e. the hoar frost. Deposition, the direct formation of solid phase of the substance from its gas phase without going through the liquid phase, is a kind of latent heat release process. Frost is a common example of deposition (Fig.1).
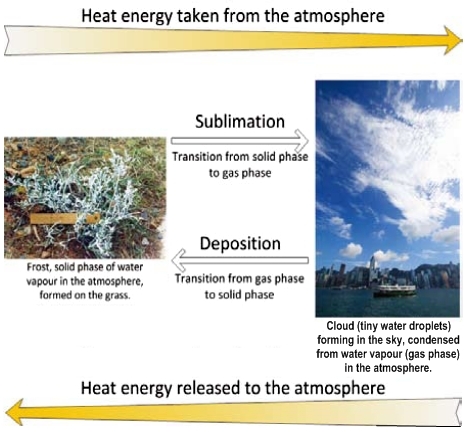
Fig.1
In addition to temperature of the surrounding air and the object itself, the amount of cloud will inhibit radiation cooling. Under cloudy conditions, radiation cooling will be weaker and is not conducive to the formation of frost. Therefore, hoar frost occurs mostly under clear nights when radiation cooling is the strongest. Wind also plays an important role in the formation of frost. If the wind is light, the air slowly flows through the cool surface and at the same time brings abundant supply of moisture which are conducive to the formation of frost. On the contrary, under strong wind condition, the air flows rapidly without good contact with the surface. The air at low levels will also mix up and is not favourable to the drop of temperature, which in turn inhibit the formation of frost.
A cycle of four seasons passed. This is the last article of the series, I hope the readers can have a better understanding of the atmosphere and appreciate the changing weather in four seasons.