Visibility observations by Light Detection And Ranging System (LIDAR)
Visibility observations by Light Detection And Ranging System (LIDAR)
CHAN Pak-wai
March 2011
The LIDAR systems at the Hong Kong International Airport are mainly used for measuring winds and detecting windshear that may be encountered by the aircraft. At the same time, they provide the backscattered power data due to suspended particulates and water vapour in the air. By combining the backscattered data and the measurements of visibility sensors on the airfield, it is possible to produce visibility maps that provide a two dimensional (2D) picture of visibility distribution inside and around the airport.
The figures below show an example on the observations of fog and mist on 8 February 2005. Figure 1 is the photo taken at the Airport Meteorological Office at about 8 a.m., showing a shallow layer of fog patches just outside the airport. The same phenomenon is displayed by the visibility map produced at that time (Fig.2). The LIDAR-based visibility maps are generated in real time for weather forecasters and observers to monitor visibility condition around the airport.

Fig.1 Fog patches
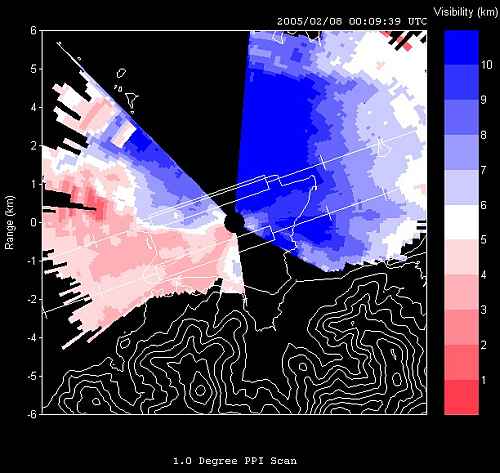
Fig.2 LIDAR-based visibility map visibility in colour scale on the right hand side