Measurement of Ultraviolet (UV) Index
Measurement of Ultraviolet (UV) Index
LAM Ming-chun
July 2024
What is UV index?
Solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation can be broadly subdivided into UVA (315-400 nm), UVB (280-315 nm), and UVC (100-280 nm). Since all UVC is absorbed by the atmosphere, only UVA and UVB reach the Earth's surface.
The UV index is a measure of the potential harm of UV radiation on the human skin. The higher the UV index, the greater the potential for damage to the skin. The recommended standard method from the World Meteorological Organization and the World Health Organization for calculating the UV Index is to measure the solar UV radiation intensity at wavelengths from 250 to 400 nanometers and multiply the intensity at each wavelength by the corresponding weighting factor in the erythemal action spectrum curve (Figure 1) to reflect the response of human skin to UV radiation. The UV index, IUV is calculated from the following formula [1]:
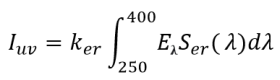
where λ is the wavelength in nm,
Eλ the UV irradiance in W/(m2 nm) at wavelength λ,
Ser(λ) the weighting factor at wavelength λ in the erythemal action spectrum, and
ker a constant equal to 40 m2/W.
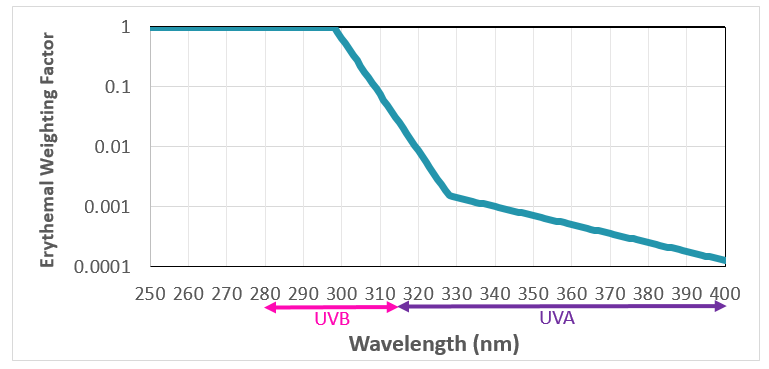
Figure 1 The erythemal action spectrum[2].
The erythemal action spectrum is a composite curve obtained by statistical analysis of research results on the response of different types of human skin to UV radiation. Figure 1 shows the erythemal weighting factor for UV radiation of different wavelengths, representing the damaging effect of the UV radiation to human skin. It can be seen that the damaging effect of UVB to the skin is much larger than that of UVA.
How is UV index measured?
The Hong Kong Observatory uses broadband UV sensors to measure the intensity of UV radiation at the King's Park Meteorological Station (Figure 2). Both the UV radiation transmitted directly through the atmosphere and those scattered by gases and particles in the atmosphere are measured. The instrument has a spectral response similar to the erythemal response spectrum and gives the total erythemally weighted UV irradiance. The UV Index is then obtained by multiplying this erythemally weighted UV irradiance by 40. To ensure data availability, an additional UV sensor has been installed at King's Park to serve as a back up. The UV index is disseminated in real-time through various channels including the Observatory’s website and “MyObservatory” app.
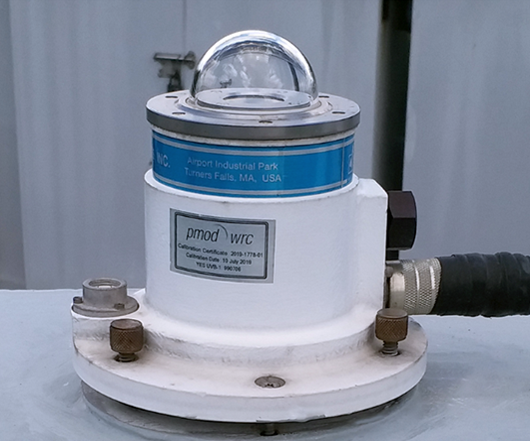

Figure 2 The broadband UV sensor at King's Park Meteorological Station.
References:
[1] World Health Organization, 2002: Global Solar UV Index – A Practical Guide.
[2] International Commission on Illumination (CIE), 1998: Erythema reference action spectrum and standard erythema dose, CIE S007/E1998.
[1] World Health Organization, 2002: Global Solar UV Index – A Practical Guide.
[2] International Commission on Illumination (CIE), 1998: Erythema reference action spectrum and standard erythema dose, CIE S007/E1998.