Sunburn and SPF
Sunburn and SPF
LEE Boon-ying
What is SPF?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor. Put simply, it relates to how long, on a sunny day, it takes to get burnt by the sun's ultraviolet (uv) radiation (let's don't worry about the sun's intensity, time of day, skin colour etc. which obviously would affect the time duration to get sunburnt). For instance, SPF 30 means that with sunscreen lotion on, it will take 30 hours to produce a detectable burn on a person who gets sunburnt in an hour.
Then, does it mean that an SPF 60 lotion offers twice as much protection as an SPF 30 one?
No. The difference in protection is only 1/30 - 1/60, or roughly 1.7%.
What SPF should I use for sunscreen lotion?
Sunscreen lotion with an SPF of 30 or above is recommended. Apply liberally and re-apply after swimming or sweating.
What other precautions should I take?
Small amounts of uv radiation are beneficial to people and essential in the production of vitamin D. However, excessive exposure to solar uv radiation may result in health effects on the skin, eye and immune system. You can check the latest uv level at:
https://www.hko.gov.hk/en/wxinfo/uvinfo/uvinfo.html
The same website also provides uv forecast for the next day for planning purpose. Apart from the use of sunscreen lotion, other protection measures include: stay in the shade, use an umbrella, wear long-sleeved and loose-fitting clothing, wear a broad brim hat and wear uv blocking sunglasses. It is particularly important to protect babies and young children from the sun.
https://www.hko.gov.hk/en/wxinfo/uvinfo/uvinfo.html
The same website also provides uv forecast for the next day for planning purpose. Apart from the use of sunscreen lotion, other protection measures include: stay in the shade, use an umbrella, wear long-sleeved and loose-fitting clothing, wear a broad brim hat and wear uv blocking sunglasses. It is particularly important to protect babies and young children from the sun.
Is it enough just to stay in the shade?
Not enough. Shade can reduce uv by 50% or more. Indoor workers receive 10 to 20% of outdoor workers' yearly uv exposure. However, sand on the beach reflects up to 15% of uv radiation. Some people get burnt while skiing because snow reflects up to 80% of sunburning uv.
Will the uv radiation be lower when there are clouds?
uv radiation levels are highest under cloudless skies. But even with cloud cover, they can also be high even in the presence of clouds. There have been occasions when broken clouds enhance uv radiation by reflection from their sides.
What else should I take note?
At half a metre under water, the uv is still 40% as intense as at the surface. Hence the need for water-proof sun lotion. UV increases by 4% for every 300 metre rise in altitude. In Hong Kong, on average over 70% of uv is received between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m. on a sunny day.
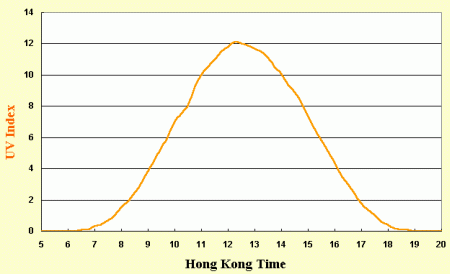
Diurnal variation of UV Index on a sunny day.
For further details on protection against uv radiation, please check out: https://www.hko.gov.hk/en/publica/gen_pub/files/uv_e.pdf.
References:
[1] Global Solar UV Index: A Practical Guide, World Health Organization, 2002.
[2] R.L. Wolke, What Einstein didn't know, Dell Publishing, 1997.
[3] Y.K. Leung et al., Solar Ultraviolet Index in Hong Kong, Hong Kong Observatory Technical Note (Local) No. 80, 2004.
[4] 'Safety under the Sun - Protect yourself against UV Radiation' - pamphlet released by the Department of Health and the Hong Kong Observatory.
[1] Global Solar UV Index: A Practical Guide, World Health Organization, 2002.
[2] R.L. Wolke, What Einstein didn't know, Dell Publishing, 1997.
[3] Y.K. Leung et al., Solar Ultraviolet Index in Hong Kong, Hong Kong Observatory Technical Note (Local) No. 80, 2004.
[4] 'Safety under the Sun - Protect yourself against UV Radiation' - pamphlet released by the Department of Health and the Hong Kong Observatory.