How to Measure Sunshine Duration?
How to Measure Sunshine Duration?
LAM Hok-yin
March 2013
Since 1950s, the Observatory has been using conventional Campbell-Stokes sunshine recorder to record the sunshine duration at King's Park. Sunshine recorder essentially consists of a glass sphere mounted in a spherical bowl and a metallic groove which holds a record card. Sun's rays are refracted and focused sharply on the record card beneath the glass sphere, leaving burnt marks on the card. As the sun traverses, continuous burnt marks will appear on the card. Observers can measure the sunshine duration based on the length of the burnt marks.
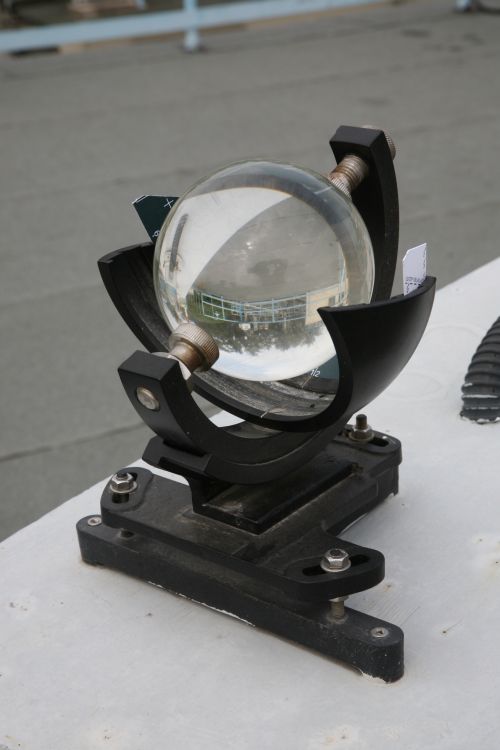

Figure 1: Campbell-Stokes sunshine recorder
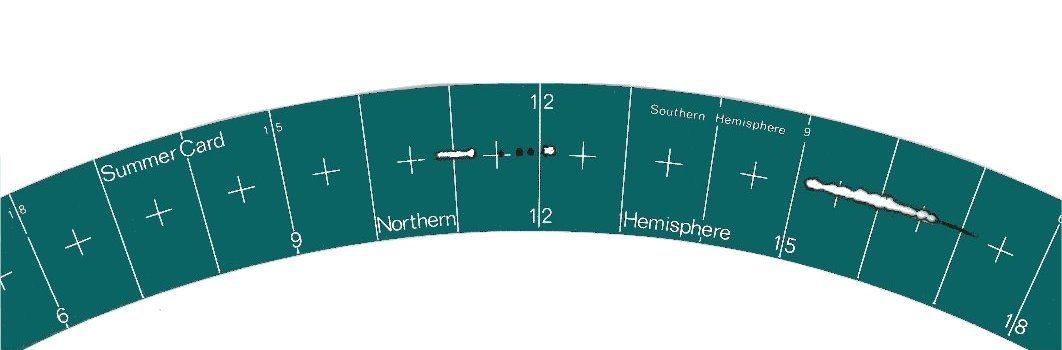
Figure 2: Burn marks on the record card
Although the design and operation of sunshine recorder are quite simple, it requires manual observations of burnt marks on record cards as well as manual change of cards. To streamline operations, the Observatory started using a fully automatic CSD sunshine meter to record sunshine duration since 2005. The sunshine meter consists of three sensors. When sunlight is detected by the sensor, it will be transformed into electricity. Solar radiation can be calculated based on the generated voltage. The sensor at the front, which is used for measuring global solar radiation, is not shaded and receives sunlight from all around. The sensors in the middle and to the rear are partly shaded. The purpose for the shading is to avoid direct sunshine for measurement of diffuse solar radiation. By using the values of global and diffuse solar radiation, the direct solar radiation can be computed and the sunshine duration can be determined according to the latest World Meteorological Organizations definition[1].

Figure 3: CSD sunshine meter
Footnote:
Sunshine duration during a given period (e.g. within one day) is defined as the sum of the time for which the direct solar irradiance exceeds 120 W/m2.
Sunshine duration during a given period (e.g. within one day) is defined as the sum of the time for which the direct solar irradiance exceeds 120 W/m2.