What is Radiation Cooling?
What is Radiation Cooling?
Maximum cooling of the ground occurs under clear skies, light winds and dry conditions. In winter, a large temperature difference sometimes exists between the urban area and the New Territories.
What causes the air temperature to rise in the daytime?
Everything radiates heat. The ground, for example, emits heat continuously to outer space while receiving energy from the sun.In the daytime, incoming solar energy exceeds the outgoing energy and the temperature of the ground surface rises (Fig. 1).
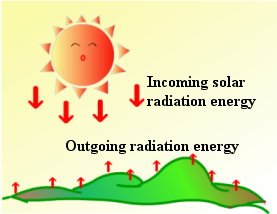
Fig.1 Ground heated during daytime
What causes the air temperature to fall at night?
At night, as there is no incoming solar energy and the ground continues to radiate away heat, its temperature falls. This night-time cooling is called "radiation cooling" (Fig. 2).
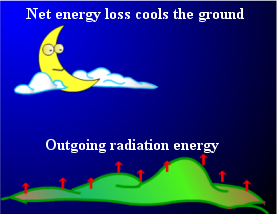
Fig.2 Radiation Cooling at night
Under what conditions will air temperature fall more appreciably at night?
The amount of temperature falls at night-time is related to cloud cover, wind strength and humidity. Maximum cooling occurs under clear skies, light winds and dry conditions.
The effect of cloud on ground temperature is akin to wrapping with a blanket to keep our body warm. Thus, under cloudy conditions the overnight temperature drop is less than that under clear skies (Fig. 3).
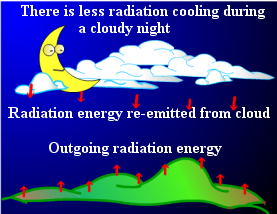
Fig.3 Effect of cloud on radiation cooling
Light winds tend to confine the cool air locally, preventing it from getting warm by mixing with surrounding air. Moisture in the air keeps the heat on the ground from radiating away. Hence, dry air cools off faster than moist air.

Fig.4 Factors affecting the extent of cooling at night
In winter, a large temperature difference sometimes exists between the urban areas and the New Territories. Why?
People often say it is cooler in the New Territories. This notion has its scientific basis. Figure 5 shows the temperature distribution in Hong Kong in the early morning of 21 December 2003. It can be seen that temperatures in the Hong Kong Island and Kowloon areas were around 10 degrees, but were below 4 degrees in the northern part of the New Territories. What causes this temperature difference?
Under clear skies, light winds and dry conditions, temperatures over exposed areas in the New Territories can drop appreciably overnight because of radiation cooling. In the urban areas, the dense population and their activities generate heat. Buildings also accumulate heat during the day. Therefore, the temperature drop in the urban areas at night-time is slower than that in rural areas. Also, temperature variation of the sea is less than that of the land, the sea surface temperature in general being higher than the average air temperature in winter (the situation reverses in summer). Temperatures in urban areas near the sea are modulated by the sea and therefore drop more slowly. Being a rural area far away from the sea, temperatures in the northern part of the New Territories cools faster in a cloud-free winter night. As such, the residents there have to cover themselves with thicker blankets.
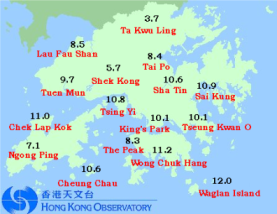
Fig.5 Minimum temperatures (oC) in the morning of 21 December 2003
"Cool Met Stuff" - Radiation Cooling (in Cantonese only)