What is Foehn Wind?
What is Foehn Wind?
HO Ka-hon
What is Foehn wind?
As the name implies, Foehn winds are dry and hot. They descend along the leeside of mountains, and are special to mountainous regions.
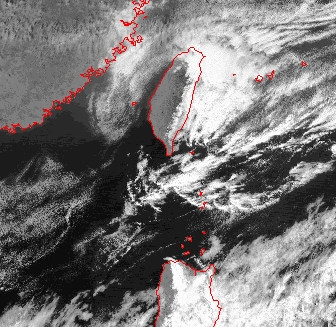
Satellite picture here shows an example of Foehn effect over Taiwan. At the time, winds were blowing from the northeast. Hence the appearance of clouds over the eastern side of Taiwan, while the western side is practically cloud-free. The same effect can be seen over Philipines. (The image was originally captured by Multi-functional Transport Satellite-1R of Japan Meteorological Agency.)
What causes Foehn winds?
Foehn winds are caused by the subsidence of moist air after passing a high mountain. The air is forced to move upslope when encounters a mountain barrier. As the temperature decreases with height, the moist air will become saturated and condense to form clouds and rain when it rises to a certain height. The amount of water vapour that remains in the air therefore decreases. After passing the ridge and descending along the leeside of the mountain, the air becomes warmer. Temperature of drier air will rise even faster. This results in dry and hot winds.
Where can we find Foehn winds?
Foehn winds are rather common in mountainous regions around the world, such as the Alps in Europe, Rockies in the United States, Tianshan and Qinling in China.
What are the effects of Foehn winds?
Apart from bringing warmer and drier weather, Foehn winds can cause serious natural disasters. They bring droughts, dry up plants and farmlands, and exacerbate forest fires. They also melt snow, causing avalanche and floods.