Meteorological Information Sharing in the 21st Century
Meteorological Information Sharing in the 21st Century
LUN Siu-hung
December 2023
Meteorological observations, forecast products and warnings, climatological and hydrological as well as earthquake related information are exchanged in real-time over the globe under the Global Telecommunication System (GTS) of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). The GTS was established under the World Weather Watch Programme of WMO in 1950s for the free exchange of meteorological information. It is a coordinated global system of point-to-point telecommunication facilities and standardised arrangements for timely collection and exchange of the aforementioned information. Nowadays, through the GTS, meteorological services can exchange data and information using various telecommunication methods, such as satellite communication, dedicated circuits and the Internet.
By late 1990s, as technology advanced over the decades, the meteorological community recognised the need for a modernised and integrated information system to enable the seamless exchange of weather, climate and water information among the community, which is of top importance to weather hazard management, disaster risk reduction, and climate monitoring and research. The development of the WMO Information System (WIS) began in the early 2000s under the collaboration, consultation and innovation of WMO Member countries. WIS is a coordinated global infrastructure for all WMO Programmes to meet the requirements for routine collection and automated dissemination of data and products, as well as data discovery, access and retrieval services for all weather, climate, water and related data produced by meteorological centres and Member countries in the framework of WMO. It has revolutionized the way data and information are shared, leading to improved weather forecasts, better support for early weather warning systems, and climate monitoring and research activities.
Alongside with the continuous growth of observational data and data created by numerical weather prediction systems, the constant increase in the flow of data to exchange and information to be disseminated to various users poses impact to the telecommunications networks. At the same time, meteorological related data was more common in cooperated use with other information in the society. More users wish to combine mobile, cloud and social media platforms to access a wider range of information sources and to collaborate in new and different ways. On the contrary, assessing the impact of weather-related hazards requires meteorological data to be combined with other socio-economic data, particularly those from crowd-sourcing. With the advancements in IT and communication in recent years, the second generation of WIS (WIS 2.0) builds upon the foundations of its predecessor while embracing the latest advancements in information technology and data management.
In WIS 2.0, user-centric is the key objective that takes into account the variety of different aspects of meteorology and responds to the growing demands for weather information in the society. The use of Web or cloud-based infrastructure as a data sharing platform greatly enhances data resilience and ensures uninterrupted access to critical weather information. Interfacing with popular web search engines makes the discovery of information much easier, and is particularly handy for the general public. The adoption of application programming interfaces and web services powered by industry standard messaging protocols provide effective means for process and exchange of data between machines over the web (Figure 1). All the above not only enables the seamless discovery and exchange of weather, climate and water information, but also promotes global collaboration on meteorological and climate research and analysis.
The Hong Kong Observatory (HKO) has recently set up a WIS 2.0 system on a public cloud and interfaced with the WIS 2.0 system operated by the China Meteorological Administration (CMA). Collaboration and partnership with CMA to develop and implement WIS 2.0 was underway.
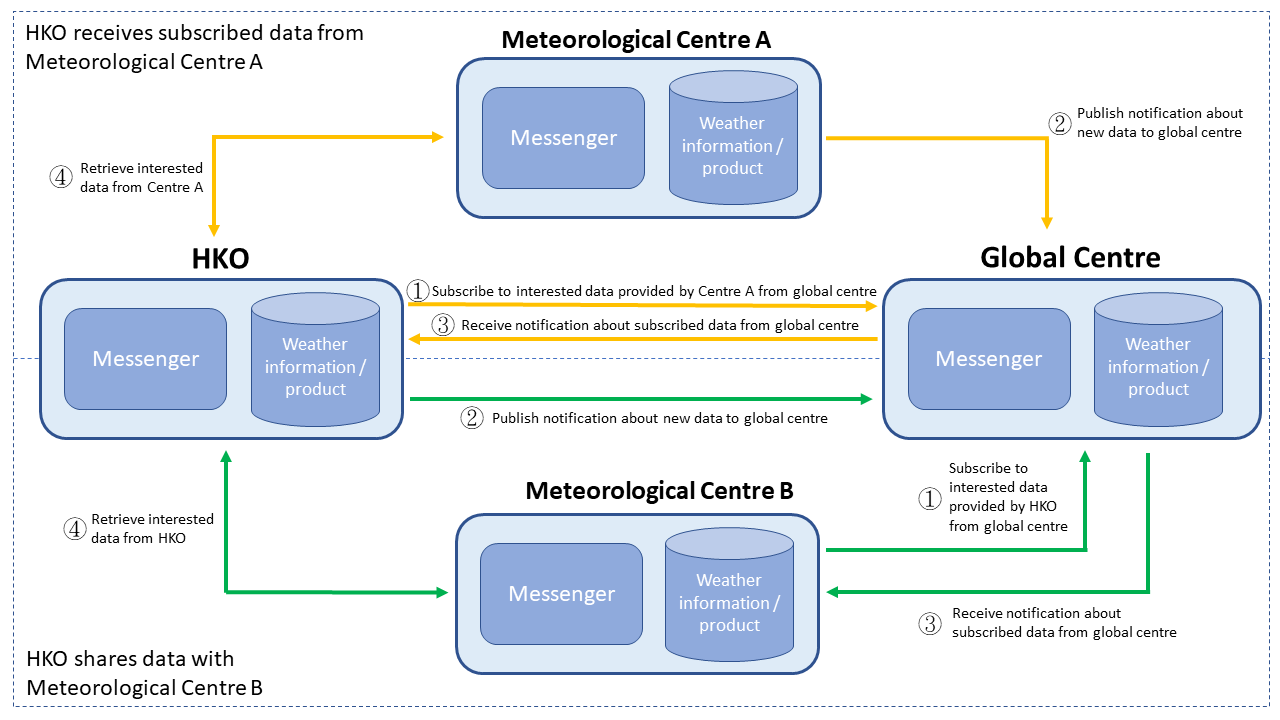
Figure 1 A conceptual diagram of information publish and subscribe under the framework of WIS 2.0.