Shock Wave
Shock Wave
CHIU Hung-yu
December 2009
A bullet travels at speed higher than that of sound. A bow-shaped shock wave will form at the nose of the bullet (Figure 1). Similarly, an aircraft flying at supersonic speed will also produce a shock wave. It results a sonic boom which can be heard.
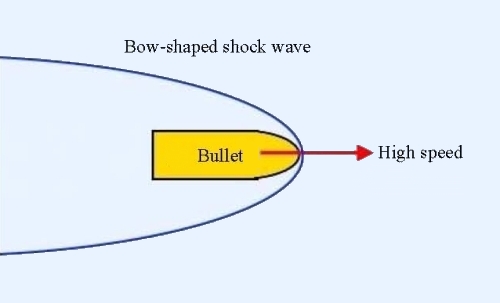
Figure 1 (Objects in the diagram are not to scale)
A yacht or kayak traversing a lake also produces a bow-shaped shock wave (Figure 2), known as bow wave. The bow wave gets larger as the yacht moves faster.

Figure 2 (Image source: Wikimedia Commons)
By the same principle, a high-speed current approaching an object can also produce a shock wave. Here is an example observed in space.
Solar wind usually travels at a supersonic speed of several hundred kilometers per second. Figure 3 shows solar wind impacting on a planet like the Earth producing a bow-shaped shock wave near the Earth. It is known as bow shock.

Figure 3 (A simplified sketch. Objects in the diagram are not to scale)
The intense solar wind causes the Earth's magnetosphere to be deformed, resulting in a tail-like feature (see figure 4).
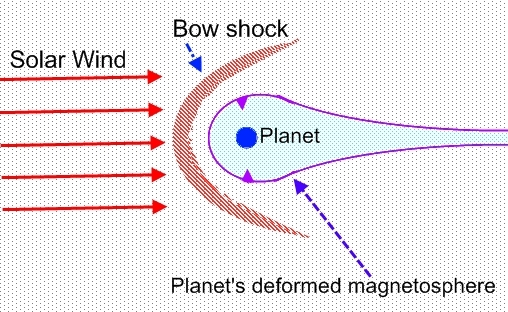
Figure 4 - A bow shock forms when the supersonic solar wind collides with the planet's invisible magnetosphere. (Objects in the diagram are not to scale)
Another example of shock wave involves charged particle moving faster than the speed of light in a medium such as water. The light emitted is known as Cerenkov Radiation which is a photonic shock wave. [see "Nature's Wonder - What is Cerenkov Radiation?"]
References:
[1] "Earth's Bow Shock in the Solar Wind", European Space Agency
[2] "THEMIS Explores the Earth's Bow Shock", NASA
[3] "Supersonic Bullet", Scientific Frontline
[4] Wikimedia Commons
[1] "Earth's Bow Shock in the Solar Wind", European Space Agency
[2] "THEMIS Explores the Earth's Bow Shock", NASA
[3] "Supersonic Bullet", Scientific Frontline
[4] Wikimedia Commons