What is a Weather Radar?
What is a Weather Radar?
RADAR stands for RAdio Detection And Ranging. Invented just before World War II for military purpose, it has since been applied to many areas, an important one being weather monitoring. Through detecting raindrops in the atmosphere, the weather radar is a very effective tool for monitoring severe weather such as tropical cyclones, thunderstorms and heavy rain in Hong Kong.
A weather radar detects rain in the atmosphere by emitting pulses of microwave and measuring the reflected signals from the raindrops. In general, the more intense the reflected signals, the higher will be the rain intensity. The distance of the rain is determined from the time it takes for the microwave to travel to and from the rain.
Doppler weather radar has become increasingly popular in recent years. It is capable of measuring the approach (or departing) speed of raindrops. The Doppler principle can be explained by noting the change in pitch of an ambulance siren. The pitch heightens as the ambulance approaches and lowers as it departs. In other words, the faster the ambulance approaches, the higher will be the pitch. For the case of a Doppler radar, the faster the raindrops move towards the radar, the higher will be the frequency (i.e. pitch) of the microwave reflected from raindrops (Fig. 1). The raindrops' approach speed is determined by the frequency shift, and provides a good estimation of the winds, which carry the raindrops.
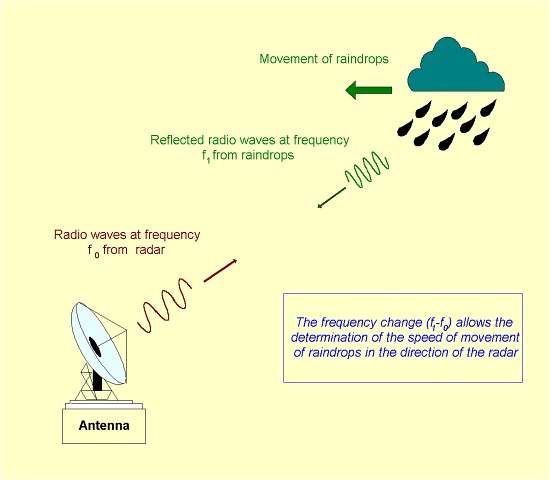
Fig. 1 Working principle of a Doppler weather radar.