Application of Virtual Satellite Images
Application of Virtual Satellite Images
TANG Wai-ho and CHAN Ying-wa
January 2023
Satellite images are indispensable for weather monitoring and forecasting. Visible and infrared satellite images are commonly used for such purpose. Image of the former type has higher resolution which enables more detailed analysis of weather systems’ features, but it is generated only during daytime when there is sunlight shining on the Earth. The latter type of image is available round-the-clock despite having a lower resolution.
With the advance of artificial intelligence technology, the Observatory has developed a deep learning model for generating virtual nighttime visible satellite images to facilitate weather forecasters in determining the centre of a tropical cyclone during nighttime. It is a conditional generative adversarial networks (CGAN) model comprising a generator and a discriminator (Figure 1). The model has been trained with past satellite images from different channels of the Himawari-8 (H-8) satellite for optimizing the performance of the generator and the discriminator. After training, real-time satellite images could be fed into the CGAN model for producing virtual visible images. Useful results were obtained as exemplified in the case of tropical cyclone Rai in December 2021 (Figure 2).
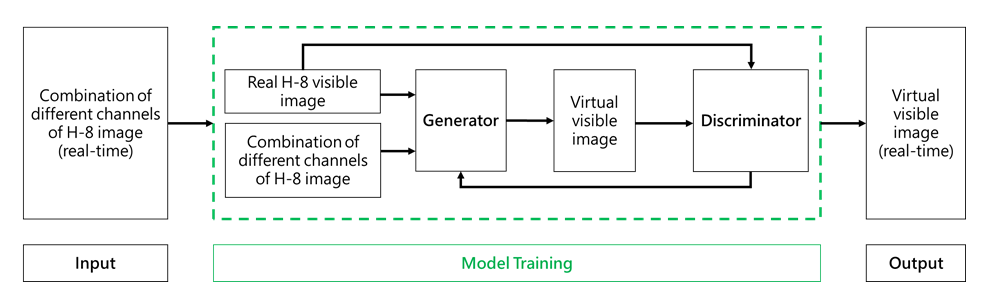
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the CGAN model generating virtual visible images.
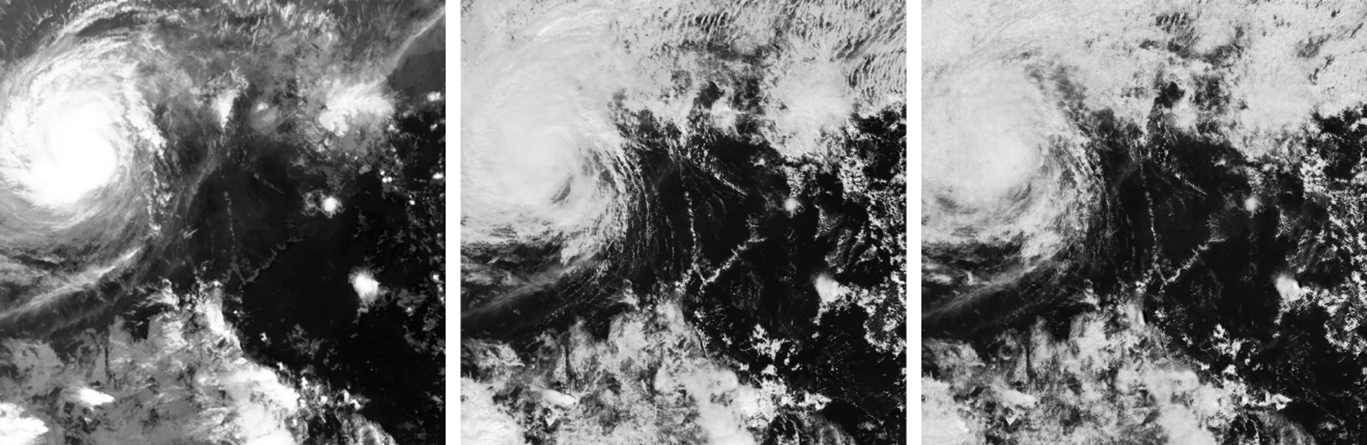
Figure 2 Satellite images captured by the Japan Meteorological Agency’s Himawari-8 satellite at 12:30 pm on 19 December 2021. From left to right are infrared, real visible and virtual visible images. Compared with the infrared image, the virtual visible image showed better banding features of clouds associated with tropical cyclone Rai when it was over the central part of the South China Sea which helped to locate the centre of Rai.
Reference:
[1] Kim K, Kim J-H, Moon Y-J, Park E, Shin G, Kim T, Kim Y, Hong S. Nighttime Reflectance Generation in the Visible Band of Satellites. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(18):2087.
[1] Kim K, Kim J-H, Moon Y-J, Park E, Shin G, Kim T, Kim Y, Hong S. Nighttime Reflectance Generation in the Visible Band of Satellites. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(18):2087.