How does a satellite measure the vertical profiles in the atmosphere?
How does a satellite measure the vertical profiles in the atmosphere?
Jeffrey LEE
July 2015
The conventional method for measuring the vertical profiles of the atmosphere is by the using the upper-air sounding system which regularly releases a weather balloon carrying a radiosonde 4 times every day (figure 1). Recently, meteorological centres have started using wind profilers and radiometers (figure 2) to enhance the upper-air observations. Such measurements are usually carried out in a sparse upper-air observation network due to high operating cost. To enhance the spatial coverage, polar orbiting meteorological satellites are now used to measure the vertical profiles of the atmosphere.

Figure 1 Automatic Upper-air Sounding System carrying a radiosonde

Figure 2 A wind profiler (left) and a radiometer (right)
How do polar-orbiting meteorological satellites measure the vertical profiles of the atmosphere?
Some of the polar orbiting meteorological satellites, such as METOP and Feng-Yun 3, are equipped with instruments (such as IASI, AMSU-A and IRAS) for measuring the vertical profiles of the atmosphere. The vertical profiles that they can measure include temperature, moisture content, as well as concentration of trace gases. These instruments, including infrared sounders and microwave sounders, perform such measurements by remote sensing.
How to measure the moisture content of the atmosphere by remote sensing?
Various gaseous molecules in the atmosphere absorb electromagnetic waves at particular frequencies. Figure 3 shows the absorption spectrum of water vapour. Kirchhoff's law of thermal radiation [1] states that the better an object is in absorbing electromagnetic wave at a particular frequency, the more efficient it is in emitting electromagnetic wave at that frequency thermally. Hence, the atmosphere also emits electromagnetic wave. By measuring the amount of electromagnetic wave emitted by the atmosphere with polar-orbiting meteorological satellites, the vertical profiles can thereby be calculated.
How to measure temperature using infrared sounders?
The hotter an object is, the more intense electromagnetic wave will be emitted. This is Stefan-Boltzmann law [2]. One example is the incandescent light bulb. The bulb will be brighter when it is hotter.
How to measure the height of water vapour in the atmosphere?
The vertical profile of the atmosphere can be obtained by taking measurements of the intensity of electromagnetic wave emitted by the atmosphere at multiple frequencies, as different frequencies can indicate the condition of the atmosphere at different heights. For example, if the measurement is taken at a frequency which is strongly absorbed by the atmosphere, the electromagnetic wave measured by the satellite will be mainly emitted from the top of the atmosphere. This is because the electromagnetic wave emitted near to the Earth's surface would be absorbed by the upper part of the atmosphere and ultimately cannot reach the satellite. On the other hand, if the measurement is taken at a frequency which is weakly absorbed by the atmosphere, satellite will then mainly measure the electromagnetic wave emitted near the Earth's surface. This is because the density of air in the lower part of the atmosphere is much higher than that in the upper part of the atmosphere. Electromagnetic wave emitted near the Earth's surface still dominates in intensity even though it is partially absorbed by the upper part of the atmosphere. By measuring various frequencies, the satellite is able to "focus" on different heights of the atmosphere. The vertical profile is then the result of integrating pieces of information obtained at different heights.
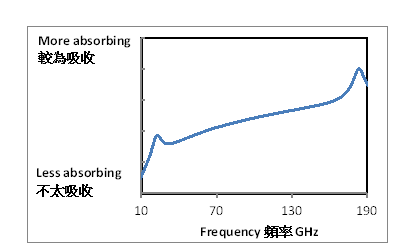
Figure 3 Absorption spectrum of water vapour
References:
[1] "Kirchhoff's law of thermal radiation", Wikipedia
[2] "Stefan-Boltzmann law", Wikipedia
[1] "Kirchhoff's law of thermal radiation", Wikipedia
[2] "Stefan-Boltzmann law", Wikipedia