Application of ADS-B Data on Aviation Weather Services
LO Chun-wing
January 2025
Aviation meteorology plays a crucial role in the safety and efficiency of air navigation. With recent advances in technology, forecasters now leverage various tools and data sources to enhance the aviation weather services, including the use of Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) data.
ADS-B is a surveillance technology used to support air traffic management. It allows aircraft to automatically broadcast their positions, altitudes, speeds, and other information via onboard systems. ADS-B relies on satellite navigation and onboard avionics, making it more precise and efficient [1].
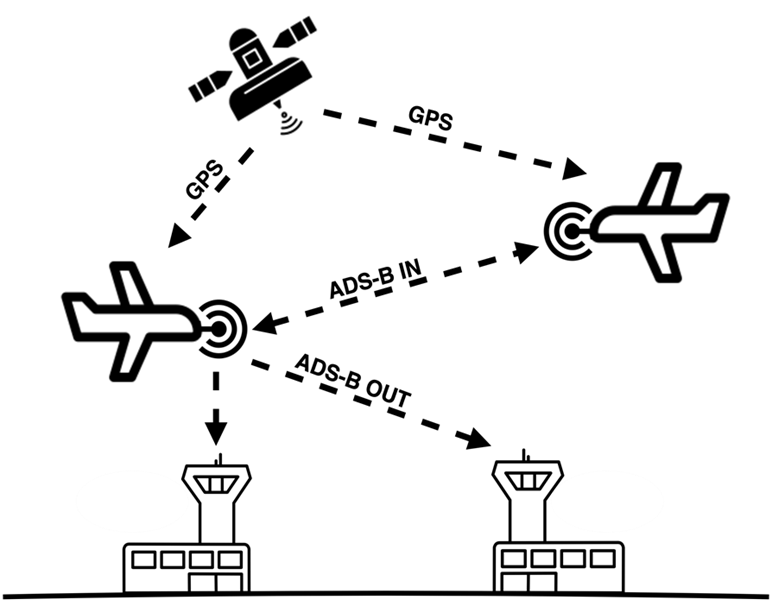
ADS-B operates in two main components (Figure 1):
- ADS-B Out: Aircraft broadcast their positions, altitudes, speeds, and other flight data to ground stations and other nearby aircraft.
- ADS-B In: Aircraft receive ADS-B signals from other aircraft and ground systems, enhancing situational awareness.
Figure 1 Illustration of ADS-B communication technology [2].
The adoption of ADS-B has enhanced the air traffic control by enabling real-time tracking of aircraft and improving surveillance coverage, particularly in remote or oceanic areas. Beyond air traffic management, ADS-B data could also be utilised in aviation weather services. The following sections describe how ADS-B data are being received at the HKO, how aviation forecasters could make use of them, and some applications of ADS-B data.
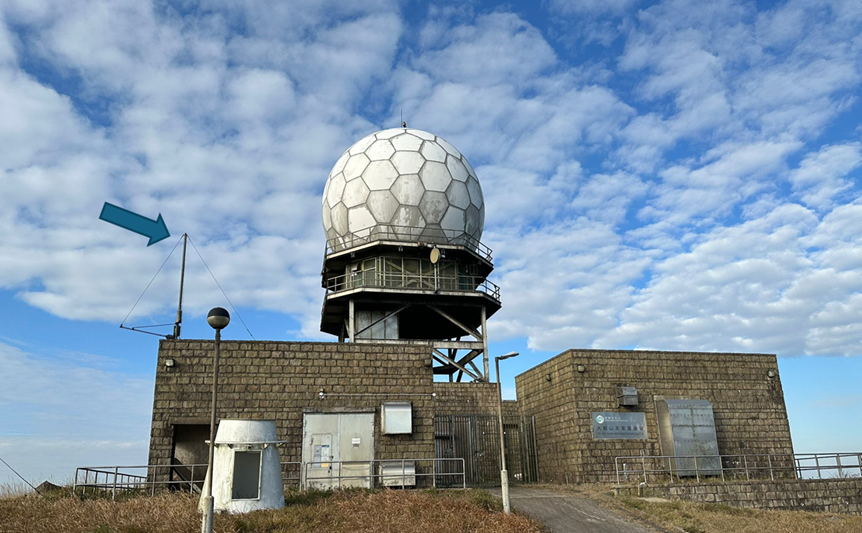
Figure 2 ADS-B antenna (blue arrow) at Tai Mo Shan Weather Radar Station.
Hong Kong Observatory installed an ADS-B receiver at Tai Mo Shan Weather Radar Station (Figure 2) in 2016, which can track ADS-B-equipped aircraft within a range of approximately 500 km. The received aircraft data are processed and shown on an integrated display interface (Figure 3).
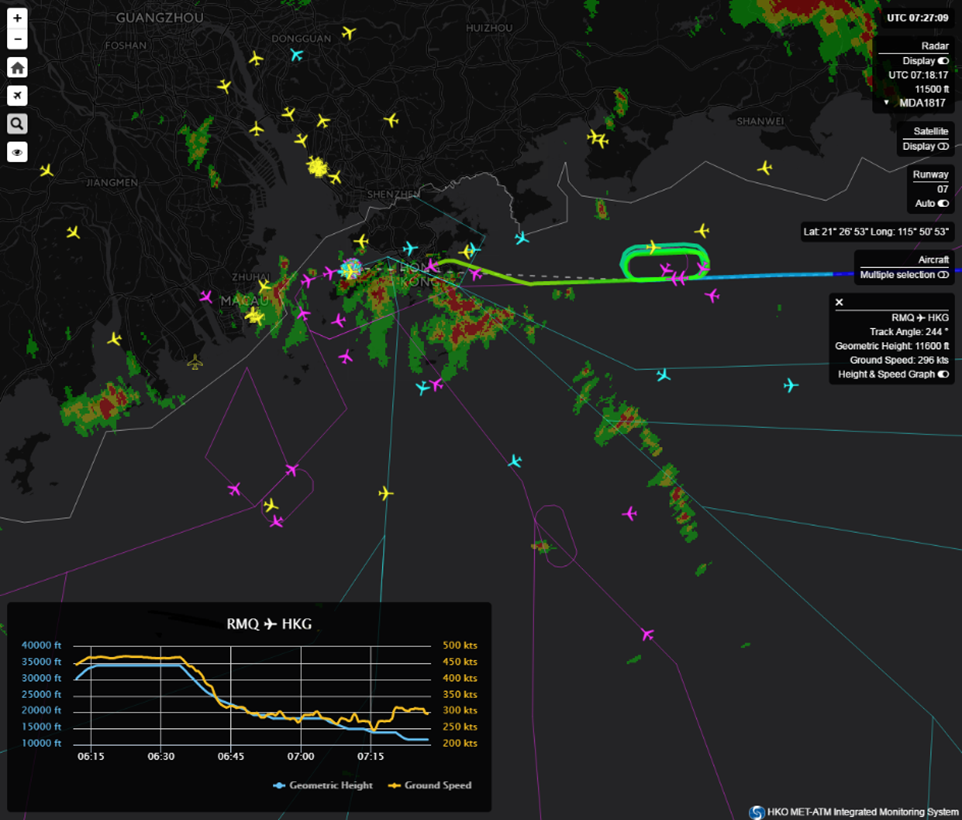
Figure 3 Aircraft positions, flight routes and weather radar imageries shown on the integrated display developed by HKO.
ADS-B data allow forecasters to monitor real-time aircraft information to support weather risk monitoring and enhance communication with aviation users about potential weather impacts. Aviation forecasters can instantly understand the impact of weather on aircraft (Figure 3), which is highly beneficial for their daily weather briefings to the air traffic control unit.
Besides real-time aircraft monitoring, another two major applications of ADS-B data in supporting aviation weather services include turbulence detection and background wind derivation. Aircraft affected by turbulence often show abrupt changes in vertical velocity and altitude. The variation of aircraft altitudes and positions can be analysed to identify turbulence areas [3], providing more supplementary observations about turbulence.
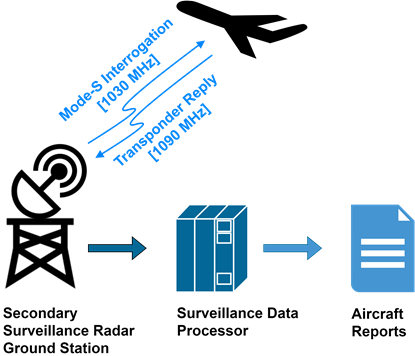
Figure 4 Mode-S interrogation by a secondary surveillance radar.
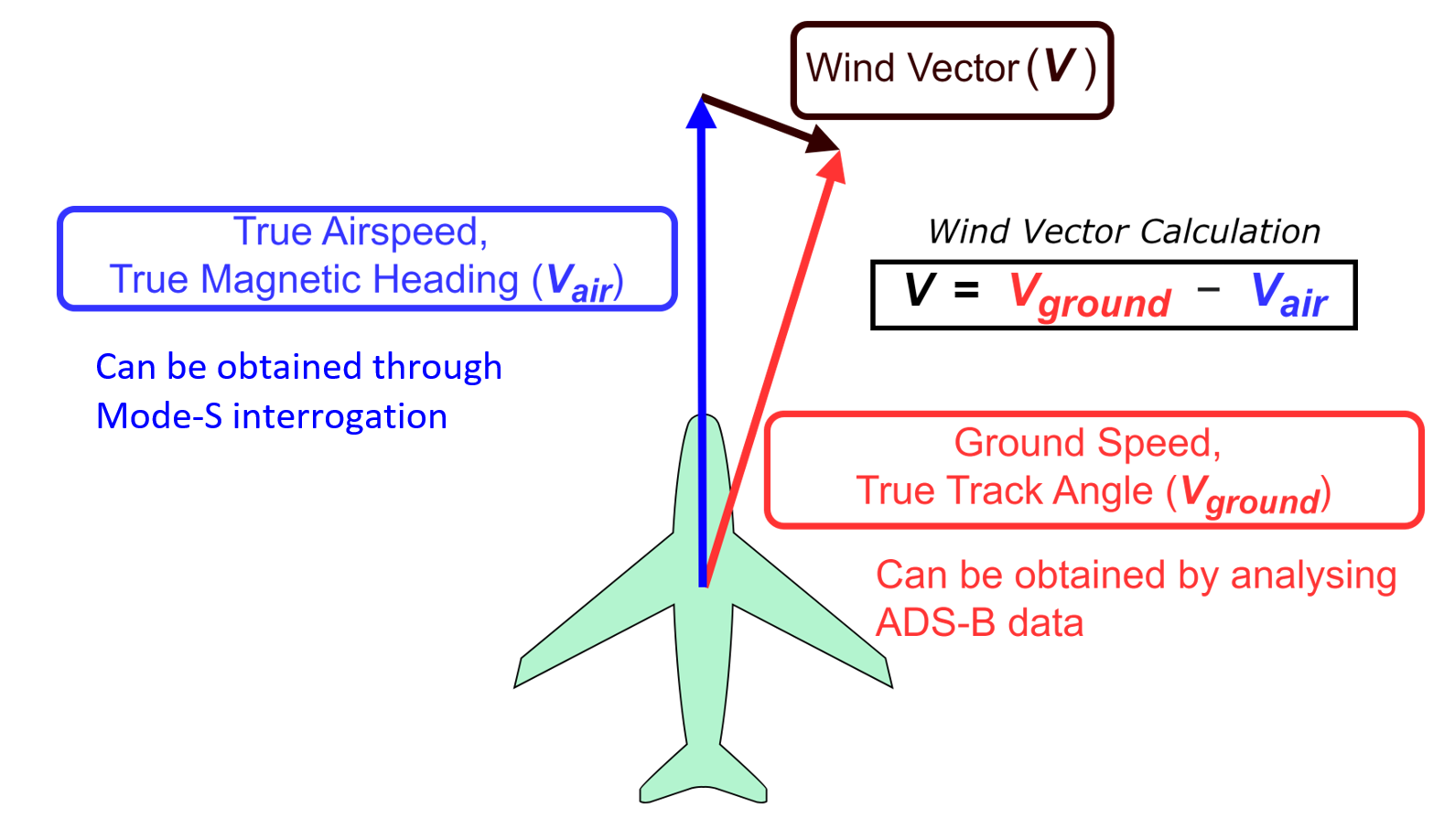
ADS-B, together with the data from Mode-S interrogation (Figure 4) performed by a secondary surveillance radar, can also be used to derive background wind information [4]. By analysing the difference between an aircraft's ground speed and true track angle obtained from ADS-B against its true airspeed and true magnetic heading obtained from Mode-S, the background wind speed and direction at various altitudes can be calculated (Figure 5), which are useful wind observations for validation of numerical weather prediction (NWP) models and improving the forecast performance of NWP models through data assimilation [5].
Figure 5 Derivation of background wind vector and its wind speed and direction using ADS-B data and Mode-S data.
References:
[1] International Civil Aviation Organization. (2020). Manual on airborne surveillance applications (Doc 9994, 2nd ed.). Montreal, Canada: ICAO. https://www.icao.int. ISBN: 978-92-9265-322-4.
[2] Viswanathan, A., & R, K. (2024). Harnessing Automation and IIoT in Air Traffic Control for Advanced Efficiency and Safety. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research in Science, Engineering and Technology, 7, 9979-9984.
[3] Leung, C. Y. Y. and Leung, H. T.: Estimating en-route turbulence using ADS-B aircraft data, EMS Annual Meeting 2024, Barcelona, Spain, 1–6 Sep 2024, EMS2024-635
[4] De Haan, S., De Haij, M., & Sondij, J. (2013). The use of a commercial ADS-B receiver to derive upper air wind and temperature observations from Mode-S EHS information in The Netherlands. Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI).
[5] WMO. (2023). ADS-B as a Source of Global Aircraft-Based Observations Data. WMO ABO Newsletter - Volume 25.
[6] Impact of assimilating Mode-S EHS winds in the Met Office's high-resolution NWP model.