What is IPCC?
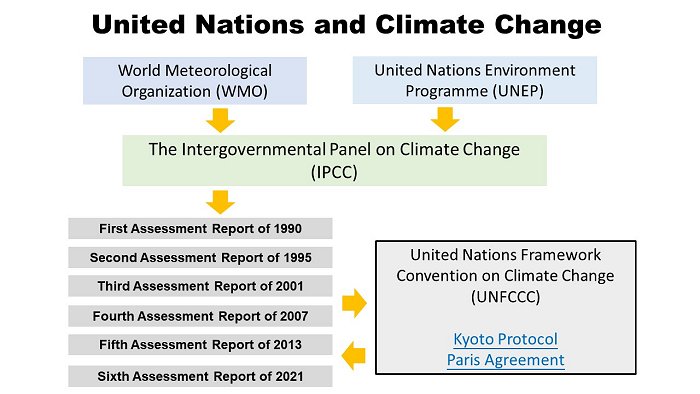
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), established under the auspices of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), is a scientific body tasked to evaluate the risk of climate change caused by human activities.
Climate change is a very complex issue. Policymakers need an objective source of information about the causes of climate change, its potential environmental and socio-economic consequences, and the adaptation and mitigation options to respond to its impacts. This is the key motivation behind the establishment of IPCC in 1988 as the authority on climate change.
The main activity of IPCC is the compilation of assessment reports and special reports. The First Assessment Report in 1990 played a decisive role in the establishment of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). The Second Assessment Report in 1995 provided key input to the negotiations of the Kyoto Protocol. The Third Assessment Report in 2001 and a number of special reports provided relevant information for the development of the UNFCCC and the Kyoto Protocol. The Fourth Assessment Report in 2007 confirmed that warming of the climate system was unequivocal. The Fifth Assessment Report in 2013 reaffirmed this finding and concluded that it was extremely likely that human influence had been the dominant cause behind the observed warming since the mid-20th century. In response to the invitation of the Paris climate conference (COP21), IPCC published the Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5℃ in 2018. The Sixth Assessment Report in 2021 clearly stated that it was unequivocal that human influence had warmed the atmosphere, ocean and land. Widespread and rapid changes in the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere and biosphere had occurred.