How do human activities contribute to climate change?
Rapid development of economic and industrial activities since the 18th century has led to excessive use of energy and resources. In particular, the burning of fossil fuels emits large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The human-induced increase in atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations enhances the greenhouse effect, resulting in global warming. The human impact on climate has exceeded the effects of other natural factors such as solar and volcanic activities.
The main greenhouse gases added through human activities, including carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide, will reside in the atmosphere for decades or even centuries. The resulting global warming and its effects are thus long lasting. As such, it is considered by scientists and policy makers to be one of the most serious problems that mankind has to face, not only now but for generations to come.
|
Ranking |
Greenhouse Gas |
Main human emission sources |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Carbon dioxide (CO2) |
Fossil fuel use and change in land use |
|
2 |
Methane (CH4) |
Agriculture and fossil fuel use |
|
3 |
Nitrous oxide (N2O) |
Agriculture |
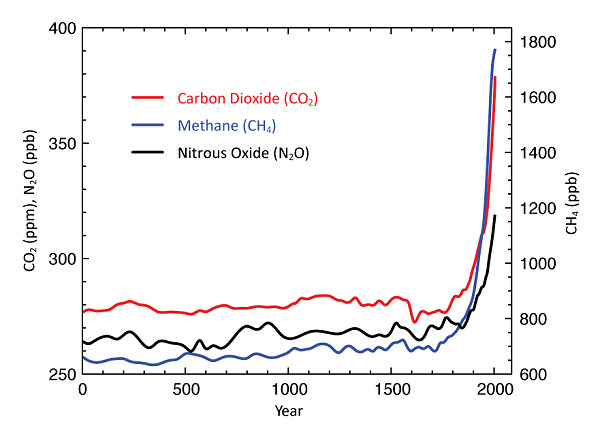
Atmospheric concentrations of key greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide) from 0 to 2005 (Source: IPCC, 2007)