The Hong Kong Observatory's Wind Shear Work Won the Civil Service Outstanding Service Award
21 September 2007
In September 2007, the Hong Kong Observatory's LIDAR Wind Shear Alerting Service won the championship of the "Specialized Service" category of the Civil Service Outstanding Service Award Scheme 2007 (http://www.csb.gov.hk/english/admin/hrm/570.html).
The LIght Detection And Ranging (LIDAR) system uses a laser beam to measure the winds up to 10 km away in non-rainy weather condition. The Hong Kong Observatory (HKO) is the first meteorological service in the world that introduced the LIDAR for airport weather alerting. Making use of the LIDAR data collected along the airport glide paths (Figure 1), HKO developed the world-first LIDAR-based wind shear alerting system and put it into operational use at the Hong Kong International Airport in 2005. HKO's achievements in the applications of the LIDAR have been reported in renowned international magazines including "Aerospace America" of the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics in late 2006 (Figure 2) and "ICAO Journal" of the International Civil Aviation Organization in early 2007 (http://www.icao.int/icao/en/jr/2007/6202_en.pdf).
The judges of the Award Scheme from both the private and public sectors commended that HKO's LIDAR project had a very clear development strategy and its LIDAR team made good use of various channels to obtain user's requirements and feedback. This project is a showcase of HKO's quest for excellence in the provision of weather services. "We are very delighted to get such positive comments from the adjudication panel of the Award Scheme. The fact that such a highly specialized project won recognition from the public is of particular meaning to us as professional meteorologists," said Mr. C.M. Shun, Senior Scientific Officer of HKO and leader of the LIDAR team. "We look forward to sharing our experience in wind shear with other meteorological services in the world", Mr. Shun added.
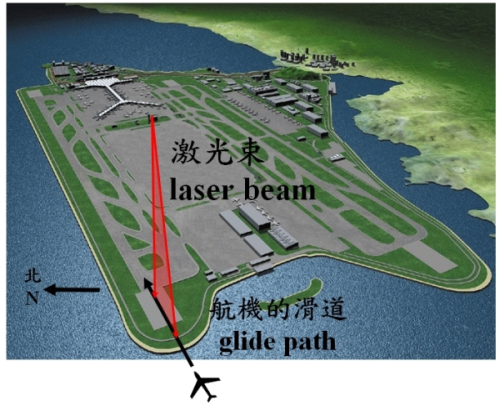
Figure 1. The laser beam of the LIDAR scans towards the airport glide paths to determine the wind shear, i.e. headwind change, to be encounter by the aircraft.

Figure 2. An article covering the LIDAR wind shear alerting system developed by the Observatory in the November 2006 issue of "Aerospace America".

Figure 3. Mr. C.M. Shun (second from the left) shared the joy of winning the championship with his teammates at the award presentation ceremony on 13 September 2007.